BERT 정리글
- BERT, Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers
BERT, Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers
Abstract
BERT는 unlabeled text를 기반으로 deep bidirectional representation을 pretrain하기 위해서 만들어졌다. 이는 모든 layer에서 왼쪽과 오른쪽 모두의 context정보를 바탕으로 만들어진다.
결과적으로 pretrained된 BERT 모델은 output layer을 추가하고 fine-tuning을 함으로써 question answering 그리고 language inference분야에서 state-of-the-art 성능을 낼 수 있다. 이는 task-specific한 구조의 변화없이 가능하다.
1. Introduction
pretrained language representation을 활용하는데는 두 가지 전략이 있다.
-
Feature-based: ELMO
task-specific한 architecture를 사용한다.
-
fine-tuning: OpenAI GPT
task-specific한 parameter를 적게 사용한다.
위의 두 가지 전략은 pretraining을 하는동안 동일한 objective를 사용하게 된다. 또한 모두 unidirectional representation을 사용하고 있다.
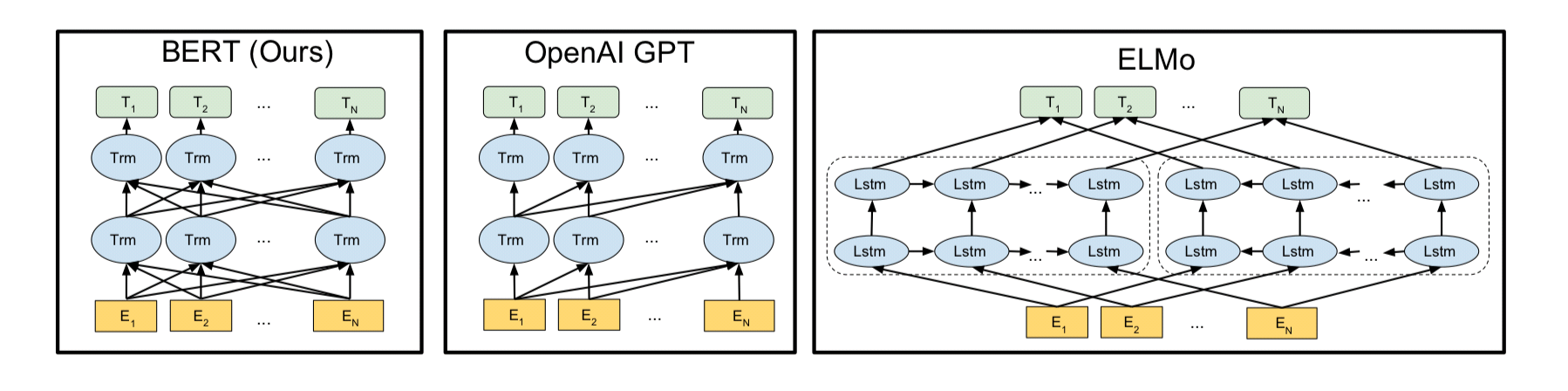
하지만, 본 논문에서는 unidirectional representation이 pretrained representation 능력을 제한한다고 주장하며, 이는 특히 fine-tuning 방법론에 영향을 많이 끼친다고 말한다. 가장 큰 한계는 standard language models가 unidirectional하며 이는 architecture를 선택할 때 많은 제한을 두게 된다. 예를 들어서, openAI GPT의 경우 left-to-right architecture를 사용한다. 모든 토큰은 self-attention layer에서 자기 자신보다 이전의 있는 토큰에만 영향을 끼친다. 이런 제한은 sentence-level task에서 sub-optimal하다.
이 논문에서는 세 가지 contribution을 제공한다.
- Bidirectional pre-training for language representation
- pre-trained representation은 task-specific architecture의 필요성을 감소시킨다.
- 11가지 NLP task에 대해서 SOTA의 성능을 보인다.
2. Related Work
pre-training general language representations에 관련된 연구들이다.
2.1 Unsupervised Feature-based Approaches
-
word embedding vectors
-
ELMO
2.2 Unsupervised Fine-tuning Approaches
word embedding parameter를 unlabeled text로 pre-trained 하는 것으로 연구가 시작되었다.
- OpenAI GPT
fine-tuning approach는 학습과정에서 적은 parameter를 학습시키면 된다는 장점을 가지고 있다.
2.3 Transfer Learning from Supervised Data
NLP, vision task에서 모두 tranfer learning은 효과적임을 보여주고 있다.
- Imagenet pretrained
3. BERT: unified architecture across different tasks.
BERT는 두 가지 단계를 가지고 있다.
-
pre-training: unlabeled data를 이용해서 학습을 진행한다.
-
fine-tuning: weight값을 pre-trained된 값으로 초기화해준다. 그 후 labeled data를 이용해서 지도학습을 진행하게 된다.
-
Model Architecture
Transformer 기반으로 만들어졌다. Transformer 논문은 encoder decoder구조로 이루어져 있지만, BERT에서는 encoder 위주로 사용한다.

-
**Input/Output Representations **
down-stream task에서 잘 작동하려면, input representation이 single sentence 혹은 a pair of sentence에 모두 유연하게 반응할 수 있어야 한다.

해당 논문은 WordPiece embeddings을 사용하였다. 첫번째 token은 항상 [CLS]이다.(special classification token의 역할을 수행) 그리고 [CLS]에 반응하는 hidden state는 classification task를 위한 representation을 모으는 역할을 수행한다.
또한 두 가지 방법으로 sentence를 구분한다.
- special token [SEP]를 이용하여 sentence를 구분한다.
- 각 sentence에 sentence embedding을 더하여 어떤 sentence정보를 가지고 있는지 알려준다.
3.1 Pre-training BERT
-
Task #1: Masked LM
직관적으로, bidirectional representation이 unidirectional representation보다 좋다는 것은 쉽게 알 수 있다. 하지만, 기존의 연구에서 사용하지 않은 이유는 바로 bidirectional representation을 하게 되면, 간접적으로 각 word가 자신에 대한 정보를 쉽게 얻을 수 있게 되며, 모델이 multi layerd contex에서 target word를 참조하기 힘들게 한다.
위의 한계점을 극복하고 deep bidirectional representation한 train을 하기 위해서 해당 연구에서는 input token중 일부를 랜덤하게 마스크하고 이렇게 mask된 단어들을 학습하도록 유도하였다. 이를 masked LM(MLM)이라고 한다. 실험적으로 약 15%의 token을 마스크하는것이 효과적이였다.
하지만, fine-tuning을 할 때, 문제가 발생한다. 바로 [Mask] 했던 token들은 fine-tuning과정에서는 발생하지 않기 때문이다. 이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위해서, 다음과 같은 조치를 취하였다.
-
i-token이 mask되었다면, 80% 확률로 [Mask]로 대체한다.
나는 학생이다. -> 나는 [Mask]이다.
-
i-token이 mask되었다면, 10% 확률로 random하게 다른 단어로 대체한다.
나는 학생이다 -> 나는 아파트이다.
-
i-token이 mask되었다면, 10% 확률로 변화시키지 않는다.
나는 학생이다. -> 나는 학생이다.
이런 조치를 취하게 되면, Transformer layer가 cross entropy loss로 학습을 진행하게 된다. 참고로 random하게 단어를 변화시키는 확률은 $0.15 * 0.1 = 0.015$ 로 모델의 표현력을 저하시키지 않는다.
-
-
Task #2: Next Sentence Prediction(NSP)
Question Answering, Natural Language Inference와 같은 task에서 두 문장 사이의 관계를 파악하는 것은 중요하다. 이는 language modeling에서 직접적으로 관계를 파악하기 힘들다. 두 문장 사이의 관계를 파악하기 위해서 해당 논문은 next sentence prediction task로 pre-train을 하였다.
- 특히 A문장과 B문장을 고를때, 50%확률로 B가 실제로 뒤에 있는 문장이다.
- 나머지 50% 확률로 random하게 배치한다.
하지만, 이전 연구에서는 sentence embedding만 down-task에 전이가 한다. (BERT는 모든 parameter를 전이한다.)
3.2 Fine-tunning BERT
- self-attention layer의 영향으로 fine-tuning은 매우 순조롭다.
- input sequence에 대해서 일정한 차원수의 representation 결과를 얻고 싶기 때문에,
[CLS]token의 Transformer output값을 사용합니다. -
[CLS]token의 벡터는 H차원을 가집니다. $C∈R^H$ - 여기서 classify하고 싶은 갯수(K)에 따라 classification layer를 붙여 줍니다. classification layer : $W∈R^{K×H} W∈R^{K×H}$
- label probabilities는 standard softmax로 계산 됩니다.$P=softmax(CWT)P=softmax(CWT)$
-
W matrix와 BERT의 모든 파라미터가 같이 fine-tuning 됩니다.
-
hyperparmeter
Batch size: 16, 32 Learning rage (Adam): 5e-5, 3e-5, 2e-5 Number of epochs : 3, 4
-
pretraining과 비교했을때, 상대적으로 fine-tuning은 적은 비용으로 학습시킬수 있다.
- fine-tuning시 dataset의 크기가 클수록 hyperparameter의 영향을 덜 받고 잘 training됨을 관측할 수 있었다고 합니다.
3.3 Comparision of BERT, ELMO and OpenAI GPT

- BERT와 OpenAI GPT는 fine-tuning approach인 반면에, ELMo는 feature-based approach이다.
- BERT와 OpenAI GPT는 유사한 pre-training방법론을 사용하였다.
- BERT와 ELMo는 bidirectional representation을 얻는다. OpenAI GPT는 unidirectional representation을 사용한다.
4.Experiments
- Fine-tunning on Different Tasks
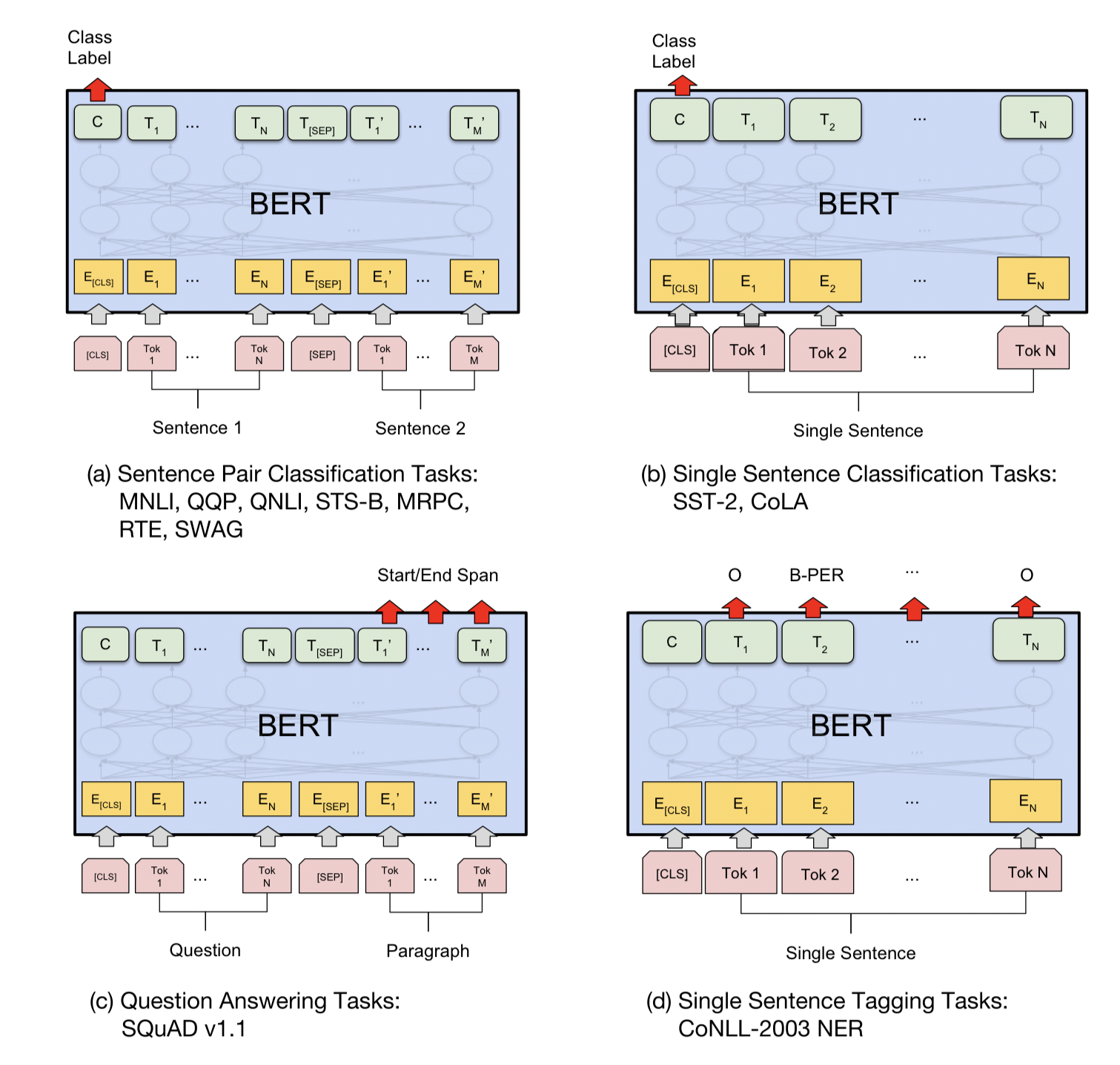
위의 그림은 각 task에 대한 fine-tuning 방법론을 시각화한 것이다. (a), (b)는 sentence level, (c)와 (d)는 token-level task이다. 참고로 [CLS]는 classification을 위한 단어이고, [SEP]는 연속적이지 않은 token을 나누기 위한 단어이다.
-
GLUE
-
SQuAD v1.1
-
SQuAD v2.0
-
SWAG